Introduction to Decarbonizing the Future
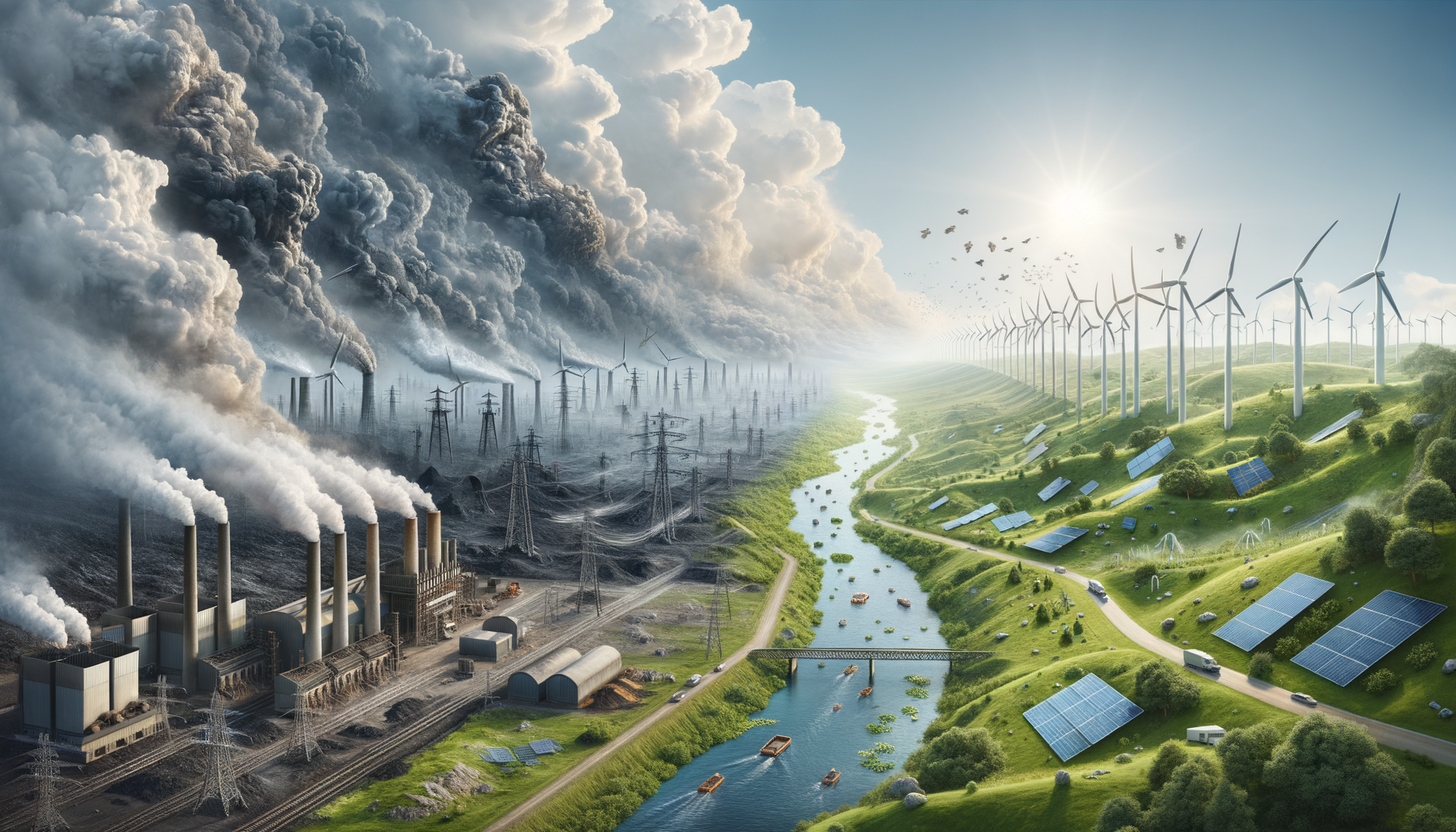
In the face of escalating climate challenges, the concept of deep decarbonization has emerged as a pivotal strategy to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Deep decarbonization refers to the comprehensive and sustained reduction of greenhouse gas emissions across all sectors of the economy, with the goal of reaching net-zero emissions by mid-century. This ambitious target necessitates transformative changes in energy systems, industrial processes, transportation, agriculture, and urban infrastructure. A systems approach to climate resilience is crucial, as it allows for a holistic view of the interconnectedness of these sectors, ensuring that solutions are sustainable and effective over the long term.
The Role of Energy Sector in Deep Decarbonization
The energy sector is a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, making it a key target for decarbonization efforts. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, is essential in reducing the carbon footprint of energy production. However, the shift is not merely about replacing fossil fuels with renewables; it requires a comprehensive overhaul of the energy infrastructure. This includes upgrading the grid to accommodate variable renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and investing in energy storage technologies. These measures are vital to ensure a reliable and resilient energy supply while minimizing environmental impacts.
Innovations Driving Energy Transition
Technological advancements are at the forefront of the energy transition. Innovations in energy storage, such as advanced battery technologies, are crucial for balancing supply and demand, especially with the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. Additionally, smart grid technologies enable more efficient energy distribution and consumption, reducing waste and optimizing resource use. The integration of digital technologies, including artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), further enhances the efficiency of energy systems by enabling real-time monitoring and management of energy flows.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Effective policy and regulatory frameworks are essential to drive the deep decarbonization of the energy sector. Governments play a critical role in setting ambitious targets and implementing policies that promote renewable energy adoption and energy efficiency. Incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs can encourage investment in clean energy technologies. Furthermore, international cooperation and agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, are vital in aligning global efforts towards a sustainable energy future. These frameworks provide the necessary support and direction for industries and consumers to transition towards low-carbon energy solutions.
Challenges and Opportunities in Achieving Net-Zero
While the path to deep decarbonization presents numerous challenges, it also offers significant opportunities. One of the primary challenges is the financial investment required to overhaul existing energy systems and infrastructure. However, this challenge is offset by the potential economic benefits, including job creation in the renewable energy sector and reduced healthcare costs associated with pollution. Additionally, achieving net-zero emissions can enhance energy security by reducing dependence on fossil fuel imports. The transition also presents an opportunity for innovation and leadership, positioning countries and companies at the forefront of a sustainable energy future.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Effort for a Sustainable Future
In conclusion, deep decarbonization of the energy sector is a critical component of the broader effort to combat climate change. It requires a coordinated approach that integrates technological innovation, policy support, and stakeholder collaboration. By embracing a systems approach to climate resilience, we can create a sustainable energy future that not only mitigates environmental impacts but also drives economic growth and enhances quality of life. The journey towards net-zero emissions is challenging, but with collective action and commitment, it is achievable.



Leave a Reply